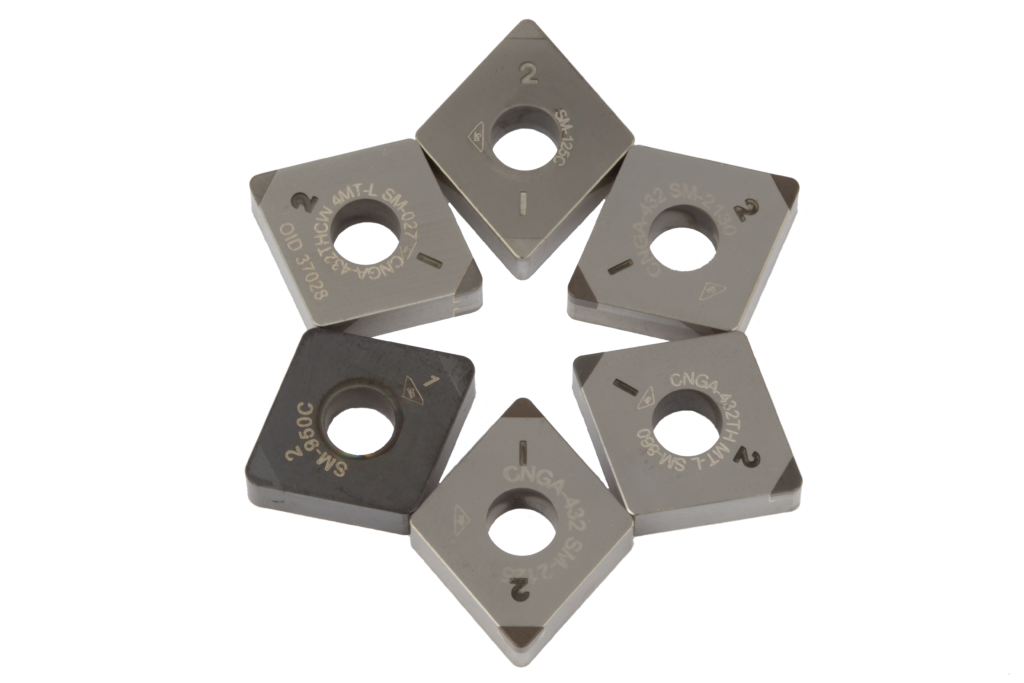

Optimized PCBN Tool Performance begins with the best PCBN Grade
Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN) is a polycrystalline (solid) form of Cubic Boron Nitride, which is the second hardest material behind only diamond. PCBN is used for the machining of ferrous materials including grey and ductile iron, powder metals, hardened alloy and tool steels. PCBN also has applications in the machining of hardened superalloys, sintered tungsten carbide, thermal sprays, hard facing alloys and HVOF coatings. With such an extensive application range, an equally extensive range of PCBN grades is required to optimize each unique application. Shape-Master Tool asks more questions about your machining processes because we have more PCBN grades available and we understand small differences in workpiece alloy, machining parameters, part design, and dimensional / surface finish requirements can significantly impact the selection of the best PCBN grade and therefore performance.
There are over 100 PCBN grades available from multiple raw material manufacturers throughout the world. PCBN grades are differentiated first by CBN content in the range of 40-95%. PCBN grades are further differentiated by secondary phases. For the hard turning grades, this constitutes ceramics including TiC, TiN, TiCN, AlTiN, Al2O3, SiN and other compounds many of which are created during the sintering process. The highest CBN content grades have secondary metal or ceramic phases. Grades are further differentiated by CBN and secondary ceramic phase particle sizes. These variations create unique toughness, abrasion resistance, crater wear resistance and thermal stability properties. PCBN grades are available as tungsten carbide backed versions for brazed tipped and fulltop tool variations as well as solid versions for solid PCBN tools and for tipped inserts using vacuum or controlled atmosphere brazing processes. Below are microstructures of a few examples (not at same magnification):
Each of the workpiece material categories listed above can be divided into different alloys, heat treatments and other variations. For example ferrous powder metal (PM) alloys include Fe-Cu, Fe-Ni, Fe-C, Fe-P, low alloy, sinter hardened, diffusion alloyed, copper infiltrated, resin impregnated, steam treated, etc. and most can be machined in the as-sintered or various heat treated conditions. Most tool manufacturers have anywhere from 2-10 PCBN grades total. Shape-Master Tool utilizes 15 PCBN grades for just the powder metal component machining industry alone.
PCBN Grade Difference Examples

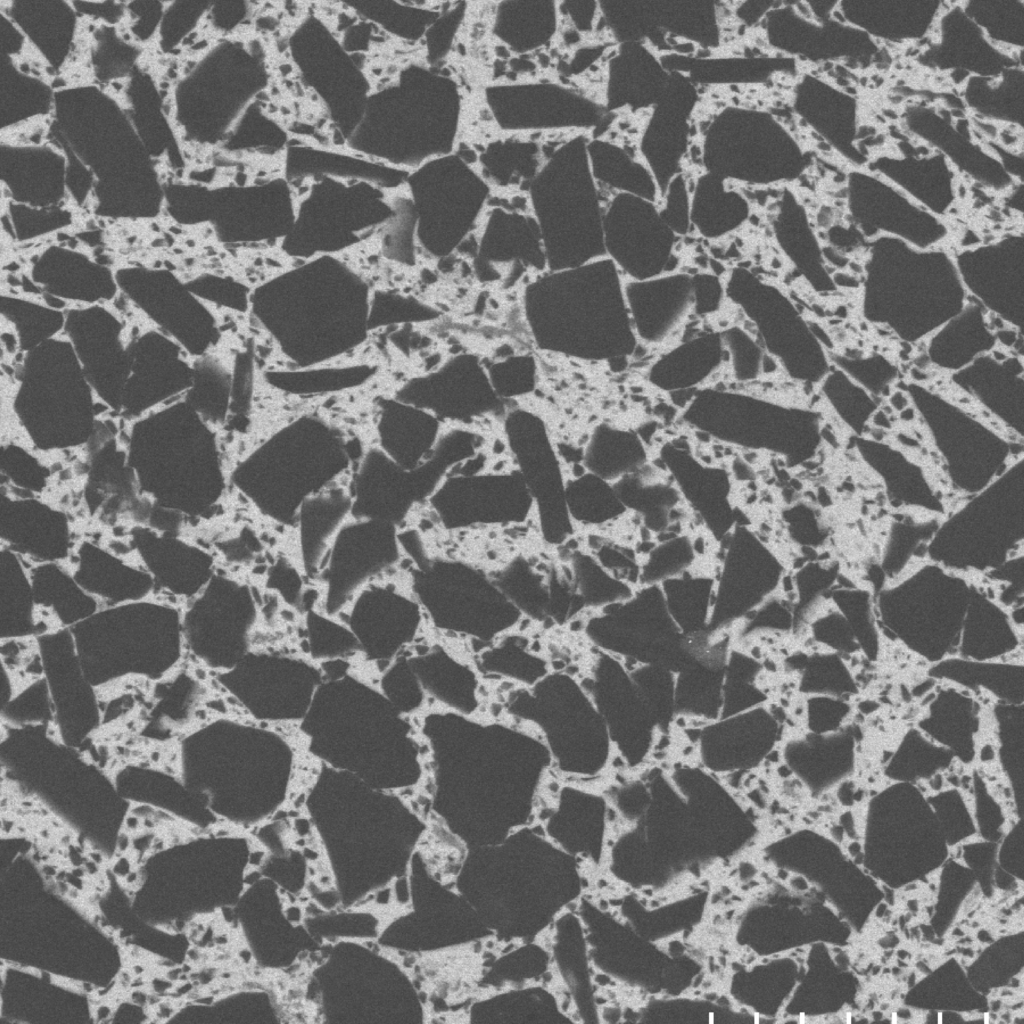
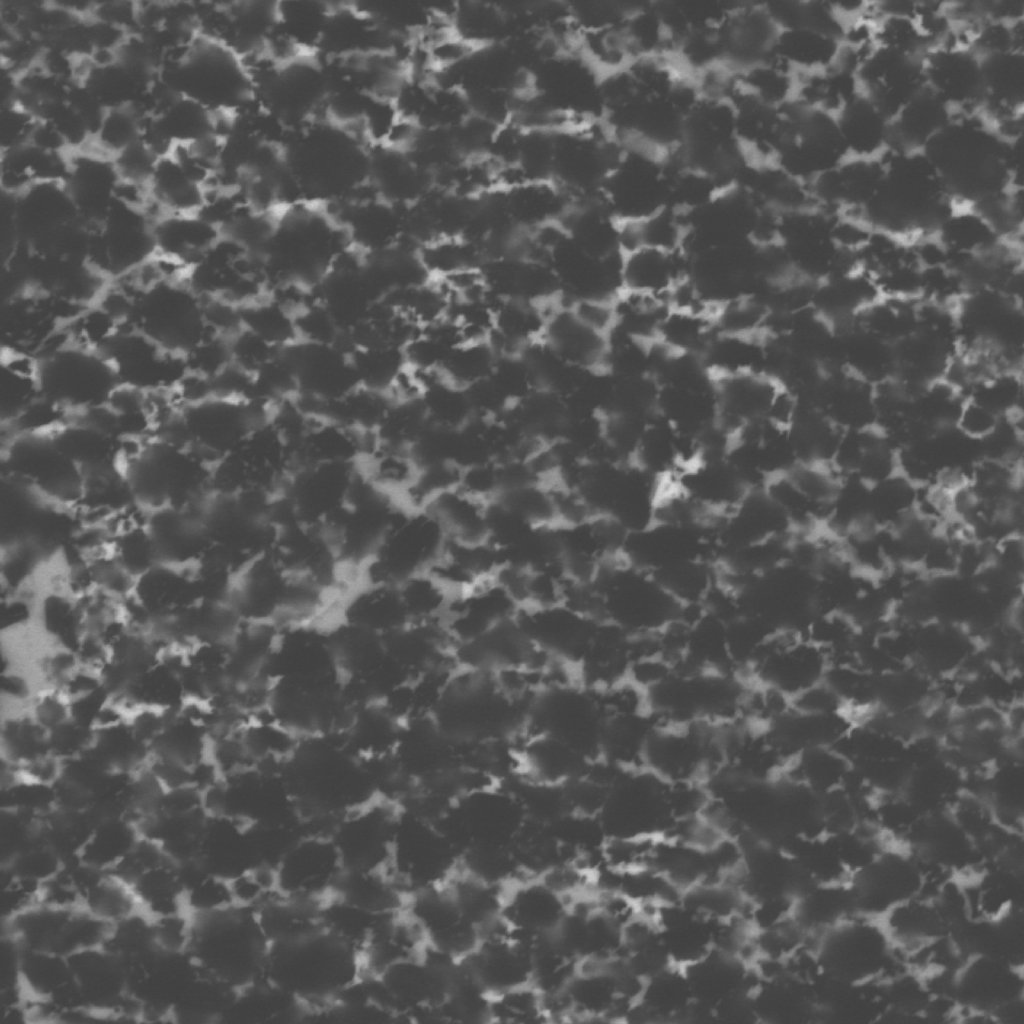
Shape-Master Tool engineers have a large selection of PCBN grades to match to your application.
Beyond workpiece alloy, PCBN grade selection is also influenced by machining parameters (speed, feed & depth-of-cut), severity of interruptions, part dimensional and surface finish requirements and coolant use. Tool performance optimization begins with knowledge of the unique capabilities for each PCBN grade and making an appropriate recommendation. Full application optimization involves selecting an appropriate insert geometry, edge preparation, radius size, rake angles plus the addition of wipers, chipbreakers and coatings as required. Optimized PCBN tools can often outperform limited selection stock standards by more than 50%. Challenging or unique applications often provide the biggest gain potential from a thorough optimization process including tests and reviewing end-of-life criteria (Ra, chipping, burrs, size, etc.) and analyzing worn tools. Complete optimization may entail multiple phases of testing of PCBN grades, edge preparations and changes to machining parameters, cut path and coolant use. Feel free to reach out to Shape-Master Tool to see if we can assist you with your tool performance and productivity gains and cost savings goals.
To learn more and optimize your machining solutions click button below: